Infertility and Homeopathy
Infertility is the inability to conceive by natural means after having regular unprotected sexual intercourse for at least 1 year. About 40% of the issues involved with infertility are due to the man, another 40% due to the woman, and 20% result from complications with both the partners.
Many cases of apparent infertility are treatable. Infertility may have a single cause in one of the partners, or it could be the result of a combination of several factors.
What causes infertility?
A couple to be gifted with a child means it is a combination of several factors that leads to a healthy baby. Unfortunately, if a couple is infertile, the reason can be either one of the partner in most cases or both the partners in few cases. So we will be dividing the causes into male and female factors for the sake of easy understanding.
Male factors that leads to infertility
Abnormal semen is responsible for about 75% of all cases of male infertility.
-
Lower sperm Quality– in a normal situation a man should have 40 million to around 300 million of sperms per millilitre of semen. A man is considered to be having very poor sperm count if his count is below 10 million per millilitre, counts of 20 million or more may be fine if motility and morphology are normal. At least 30 % of the sperms should have the normal structure and shape to be fertile and at least 50 % of the sperms should be actively motile. Abnormal sperm production or function can be due to various problems, such as undescended testicles, genetic defects, health problems including diabetes, prior infections such as mumps, trauma or prior surgeries on the testicles or inguinal region. Enlarged veins in the testes can increase blood flow and heat, affecting the number and shape of sperm.
-
Problems while delivering the sperm - such as premature ejaculation, absent ejaculation, semen entering the bladder instead of emerging through the penis during orgasm (retrograde ejaculation), delayed ejaculation, certain genetic diseases, such as cystic fibrosis, structural problems, such as blockage of the part of the testicle that contains sperm (epididymis), or damage or injury to the reproductive organs can also leads to infertility
-
Tobacco and alcohol - Male smokers have approximately 30% higher risks of infertility. There is increasing evidence that the harmful products of tobacco smoking kill sperm cells. Alcohol affects reproduction in both men and women in a number of ways. The more you drink, the greater the effect it can have on your fertility. While many of alcohol’s effects on reproduction are temporary, regular drinking over the time can lead to serious infertility problems. Besides smoking and alcohol, Overexposure to certain chemicals and toxins, such as pesticides, radiation, marijuana, and steroids (including testosterone) can leads to impaired sperm production.
-
Lifestyle factors – improper diet, lack of exercise, obesity, being underweight, junk foods, over intake of caffeine, all have contributed to the increase in infertility cases in the recent years.
Female factors that leads to infertility
For a woman to conceive, certain things have to happen: intercourse must take place around the time when an egg is released from her ovary (ovulation); the system that produces eggs has to be working at optimum levels; and her hormones must be balanced.
-
Ovulation disorders – Reproduction is controlled by a system that includes the hypothalamus (in the brain), pituitary gland, ovaries, and other glands, such as the adrenal
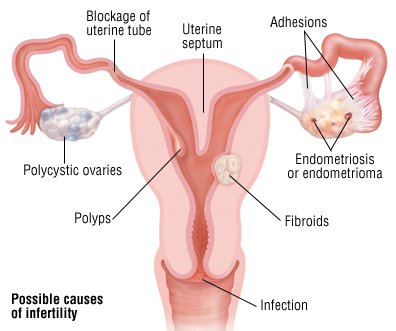 glands and thyroid gland. Problems with ovulation results when one part of this system malfunctions. Polycystic ovary (PCO) which is usually characterized by excess weight and excess production of male hormones by the ovaries is another major reason for ovulatory disorders. PCO is the leading reason of infertility among females now.
glands and thyroid gland. Problems with ovulation results when one part of this system malfunctions. Polycystic ovary (PCO) which is usually characterized by excess weight and excess production of male hormones by the ovaries is another major reason for ovulatory disorders. PCO is the leading reason of infertility among females now. -
Fallopian tube blockage - Blockage to the fallopian tubes (which carry the eggs from the ovaries to the uterus) can prevent contact between the egg and sperm. Pelvic infections leads to inflammation of fallopian tube (salpingitis), endometriosis, and pelvic surgeries may lead to scar formation and leads to fallopian tube blockage.
-
Cervical causes - Sperm must swim in the cervical mucus traveling from the vagina through the cervix and into the uterus. The mucus must provide nutritional support for sperm and be of the correct consistency. Too little or "sticky" mucus can interfere with sperm transport causing infertility. Sometimes anti-sperm antibodies are found in the cervical mucus. These are antibodies produced by the female that mistake sperm for invading pathogens. When these antibodies are present numerous "dead" or immobile sperm are seen in the post coital test.
-
Uterine causes – Benign tumours in the wall of the uterus (uterine fibroids) may rarely cause infertility by blocking the fallopian tubes. Uterine malformations and uterine polyps also contribute to female infertility.
-
Pelvic adhesions - bands of scar tissue that bind organs after pelvic infection, appendicitis, or abdominal or pelvic surgery.
-
Lifestyle factors – use of tobacco, alcohol, improper diet, lack of exercise, obesity, being underweight, junk foods, over intake of caffeine, all have contributed to the increase in infertility cases in the recent years.
-
Besides these problems, thyroid complaints, cancer and its treatment, certain medications also causes infertility in some cases
-
Unexplained infertility - The cause of infertility in approximately 20% of couples cannot be determined using the currently available methods of investigation.
Does age affects your chance of getting pregnant?
Yes, Female age is an important factor when considering probability for getting pregnant. The real issue is egg (ova) quantity and quality - which translates into embryo after fertilization. As women wait longer to have children, more couples have fertility problems due to declining egg quality, and other issues that are more common in older women. Fertility starts to decline for women from about the age of 30, dropping down more steeply from the age of 35. As women grow older the likelihood of getting pregnant falls while the likelihood of infertility rises. Most women will be able to conceive naturally and give birth to a healthy baby if they get pregnant at 35 years old. After 35 years, the proportion of women who experience infertility, miscarriage or a problem with their baby increases. By the age of 40 only two in five of those who wish to have a baby will be able to do so naturally.
From a purely biological perspective, it's best to try to start a family before you're 35 years old.
As far as Men is concerned, contrary to the popular belief, age affects the chances of fertility. As men ages, the volume of semen and sperm motility decreases. After 45 years of age, the time to pregnancy increases 5 fold as compared when he was at 25 years of age.
How to detect the cause for infertility?
There are several ways to find the exact cause of infertility through various infertility tests. But even with the most advanced techniques and medical knowledge, even now 20 % of the cause of infertility are still unknown. Fertility testing and investigation can be a lengthy process, and female fertility decreases with age, so it is best to make an appointment early on.
Tests for men
-
⇒Physical examination- your doctor will check your testicles and penis for any possible lumps, swellings or deformities.
-
⇒Semen analysis – your semen will be tested to determine whether you have a low sperm count, low sperm mobility or abnormal sperm
-
⇒Hormone testing. A blood test to determine the level of testosterone and other male hormones is common.
-
⇒Trans-rectal and scrotal ultrasound. Ultrasound can help your doctor look for evidence of conditions such as retrograde ejaculation and obstruction of the ejaculation duct.
Tests for women
For women, a number of tests can be used to try and establish the cause of infertility.
Tests for ovulation- a women to get pregnant, she needs to release an egg (ova) each month. If the women is having some irregular menstrual periods, it is advisable to check if she is ovulating. There are several methods to detect ovulation in women
- ⇒A urine test at home (using the ovulation test kit available at market) can detect luteinizing hormone (LH), which appears in high levels in the urine just before ovulation.
- ⇒A sample of your blood can be tested for a hormone called progesterone, to check whether you are ovulating. The timing of the test is based on how regular your periods are.
- ⇒If you have irregular periods, you will be offered a test to measure hormones called gonadotrophins, which stimulate the ovaries to produce eggs.
- ⇒A woman can check her body temperature each morning. Basal body temperature rises a bit just after ovulation. By checking her body temperature each morning, a woman can detect this rise, showing her ovulation pattern over months.
Tests for reproductive organs - The uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries must all be working well in order to get pregnant. There are several procedures to test these organs. Your doctor may advice you to go for
- ⇒Hysterosalpinography test- to detect any tubal blockage or to find any defect in uterus
- ⇒Pelvic ultrasound scanning- to find the size, shape and structure of the ovaries and uterus. The doctor may also advise you to undergo a follicular tracking ultrasound scanning, in which 1-3 consecutive scans are performed on specific days, depending on your menstrual cycle, to study the size and number of follicles, there by confirming the process of ovulation.
- ⇒Hysteroscop- A thin, flexible tube with a camera on its lighted end is threaded through the cervix into the uterus. The doctor can see problems with the uterus, and take tissue samples if needed
Post coital test – this test is performed shortly after having sex, while the sperms are still in your cervix. This test helps you to detect if your body is acting against the sperms, by developing anti-bodies against them.
What are the treatments for infertility?
Homoeopathy assisted reproductive treatment (HART) is widely popular for its high rates of success, economical and patient friendly compared to conventional treatment methods including assisted reproductive treatment (ART). As the cause and reason for infertility differs for male and female, so do the treatment options
Treatment for Males
Depending on the cause of infertility, the Homoeopathic treatment plans for men vary from :
-
⇒Treating sexually transmitted diseases (STD’s) – e.g. chlamydia, gonorrhoea
-
⇒Treatment of sexual intercourse problems – e.g. premature ejaculation, erectile dysfunction
-
⇒Improving the semen quality
-
⇒Treating the underlying cause - e.g. varicocele
-
⇒Counselling and treatment for DE addiction of alcohol, tobacco or other harmful drugs
-
⇒Advices on specific diet and regimen
Treatment for Female
Homoeopathy has a very high reputation in treating various female problems causing infertility by:
-
⇒Treating various hormonal problems, thus correcting the menstrual cycle and the ovulation in a natural way
-
⇒Treating various ovarian, cervical, uterine and other diseases causing infertility like polycystic ovary, endometritis, pelvic adhesions, fibroid tumours etc.
-
⇒Psychological support and treating the emotional aspects, anxiety, depression and other stress related to infertility
-
⇒Helping the patients to cope up with Assisted Reproductive Treatment
What is Assisted Reproductive Technique?
If a women does not become pregnant even after medical or surgical treatment, she may have to undergo more complex procedures called assisted reproductive techniques (ART) to get pregnant. It involves any procedures in which the ovum and sperms are handled manually. Success rates for ART varies from 25-30 %. So it is always advisable to undergo medical treatment prior to ARTVarious ART techniques involve:
Artificial insemination (AI) - Artificial insemination involves sperm being placed into a female's uterus (intrauterine) or cervix (intra cervical) using artificial techniques rather than by sexual intercourse.
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) – this is the most common form of ART being used today. It involves a process in which and egg is fertilised with sperms outside the human body in a laboratory setup. For this purpose, a healthy sperm and a mature ovum is selected which is fertilised in a laboratory dish, and then culture them for 2-6 days before being implanted in a female uterus.
Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) – in this procedure a single healthy sperm is directly injected into the egg. This technique is useful when the quality and the quantity of semen is less.
Assisted Hatching- this is a comparatively newer technique in which the implantation of embryos, which are still in laboratory, into a women’s uterus by creating a hole in the outer layer of embryos so that the embryonic cells can easily hatch out. This technique is particularly useful in women above 35 years or those with failed IVF or ICSI treatments. Assisted hatching has been associated with an increased risk of monozygotic (identical) twins.
Human Leucocyte Antigen (HLA) transfer – in cases of continuous failure of IVF treatments, transfer of Husband’s leucocyte antigen into the wife using special techniques has been found to be helpful in improving the chances of IVF and other ART treatments
In our clinics we give special assistance and care for all couples under treatment for infertility. Our Infertility treatment Protocols involves psychological support and special dietary advices to the care for the mother during pregnancies and fitness advices for a natural delivery of child.

